Transportation Models Updates and Expansion

We have developed two primary models, Truck Choice Model (TCM) and Transportation Transition Model (TTM) to better understand the effects of new technologies and fuels on trucks and LDVs. We plan to update, expand, and better integrate the model components.
Find more information here
Truck ZEV Mandate Analysis

The California Air Resources Board staff is planning to submit a proposal to their Board defining a ZEV mandate for trucks. Trucks differ greatly from light-duty vehicles in that there are many more truck types and applications; therefore, crafting an appropriate truck ZEV mandate must include consideration of more issues than for a LDV mandate.
Find out more here
Residential Deliveries: Can City Logistics Be Sustainable?
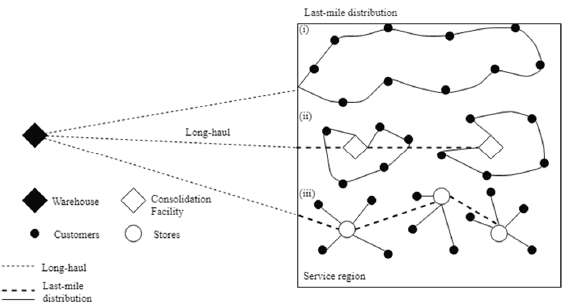
In the last decade, e‐commerce has grown substantially, increasing business‐to‐business, business‐to‐consumer, and consumer‐to‐consumer transactions. As a result, there has been a continuous growth in last mile operations, especially deliveries to residential areas, bringing along externalities such as congestion, air and noise pollution, and energy consumption. Read more here
Truck Choice Model

Zero emissions trucks, such as electric and hydrogen fuel cell trucks, would need to be adopted at a large scale and at a rapid pace in order to achieve CO2 reductions targets but that is unprecedented for trucks anywhere in the world to date. Many truck models create new technology market penetration scenarios through minimizing cost or in an ad-hoc manner. This model utilizes a fleet decision choice process based on real world factors identified through discussions with trucking fleets. These factors include capital and operating costs, uncertainty (risk), model availability, refueling inconvenience, green PR (perceived benefit of environmentally beneficial technologies), and various incentives.
Read more here
Optimizing Last Mile Operations in Fleets

Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP) is a classic operations research problem, wherein the objective is to find the set of routes that minimize the transportation cost for a fleet of vehicles departing from a depot, visiting a set of points (customers), each demanding certain quantity of goods. These delivery vehicles may have a fixed capacity and each route may be constrained to a threshold (based on time or distance).
Read more here